HOOKE'S LAW Introduction In physics, Hooke's Law is one of the fundamental principles governing how objects deform under external forces . Named after the 17th-century British physicist Robert Hooke, this law provides a crucial understanding of the behavior of elastic materials, such as springs and rubber bands. Whether stretching a rubber band or compressing a spring, Hooke's Law helps explain what happens when forces act on these materials. What is Hooke's Law: Hooke's Law states that the force F needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance x is proportional to that distance. Mathematically, it is expressed as: F= -kx Here k represents the spring constant, which is the measure of the stiffness of the spring, and x is the displacement from the displacement position. The negative sign indicates that the force exerted by the spring is in the opposite direction of the displacement. Understanding the Spring Constant: The spring constant k is a critical co...
Standard of Length, Mass And Time
Standard:
What is Standard why it is necessary to set a Standard while measuring any physical quantity?
So basically before 160, different systems of units were established/introduced and almost every system of unit has different unit for the base quantities.
For Example:
In CGS the units for base quantities were like;
Mass was measured in Grams.
Length was measured in Centimeter.
Time was measured in Seconds.
In MKS the base quantities were measured by:
Mass was measured in Kilogram.
Length was measured in Meter.
Time was measured in Seconds.
And in FPS these base quantities were measured in:
Mass was measured in Pound.
Length was measured in Foot.
So, there were difficulties whether which unit should be preferred for accurate measurement and therefore after 1960, International S.I stem of Units were introduced and 7 fundamental quantities were introduced with their standard Units.
So, Standard is defined, "Standard in measurement is a prioritized unit can be said which is ysed for measurement of a quantity across the world. Means any quantity having standard unit will be measured in that unit in the world."
For Example:
Standard of Mass is Kilogram so mass is measured in Kilogram everywhere.
Standard of Length:
In S.I Units the unit of length is meter.
Length is defined as "The minimum gap between two points lying on the same plane."
Standard of Length can be defined as, "The length of path travelled by light in vacuum during the time interval of 1/299,792,458 of a second."
Some Length Equivalents:
Some Length Measuring Instruments:
Standard of Mass:
The S.I unit of Mass is Kilogram.
It is mass of Platinum-Iridium cylinder kept at the International Bureau of Weights and Measures near Paris.
The Kilogram is the mass of special cylinder about 39mm tall that serves as the world's mass standard.
Some Mass Equivalents:
Some Mass Measuring Instruments:
Before 1960, time was measured by Mean Solar Day by 1900.
Later in 1967 standard of time was redefined to acquire accuracy using a digital clock which takes the characteristics of frequency of Cesium atom 133.
"The time is redefined as 9,192,631,770 times the period of vibrations of radiations from the cesium atom-133. ''
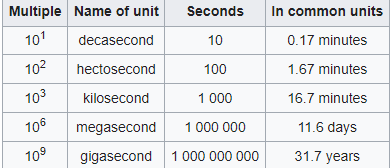
Some Time equivalents:





Comments
Post a Comment